EMF of a Cell
An electric cell is a source of energy that maintains a continuous flow of charge in a circuit. It changes chemical energy into electrical energy. It has two electrodes, positive electrode and negative electrode as shown below.
Electric cell has to do some work in maintaining the current through a circuit. The work done by the cell in moving unit positive charge through the whole circuit (including the cell) is called the electromotive force (emf) of the cell.
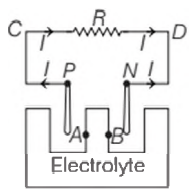
For the given circuit, if the cell has an emf of `2 V` and the internal resistance of this cell is `0.1Omega`, it is connected to resistance of `3.9 Omega`, the voltage across the cell will be
Options:
(a) 1.95V
(b) 1.5V
(c) 2 V
(d) 1.8V