Wheatstone Bridge
In 1845 by German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff described Kirchhoff’s circuit laws which are two equalities that deal with the current and potential difference (commonly known as voltage) in the lumped element model of electrical circuits.
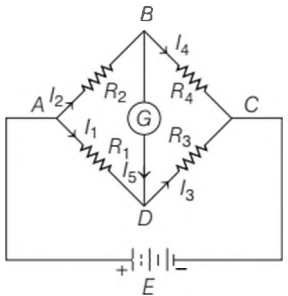
As an application of these laws, consider the circuit shown below, which is called the Wheatstone bridge. This bridge consists of four resistors `R_1, R_2, R_3 and R_4`. Across one pair of diagonally opposite points (A and C in the figure) a source is connected.
This (i.e., AC) is called the battery arm. Between the other two vertices, B and Z), a galvanometer G (which is a device to detect currents) is connected. This line, shown as BD in the figure, is called the galvanometer arm. Of special interest, is the case of a balanced bridge where the resistors are such that `I_g =0`.
Kirchhoff’s junction rule is a consequence of conservation of
Options:
(a) momentum
(b) mass
(c) energy
(d) charge