Faraday’s Laws
According to the Faraday’s first law, whenever the amount of magnetic flux linked with a circuit changes, an emf is induced in it. Induced current is determined by the rate at which the magnetic flux changes.
Mathematically, the magnitude of the induced emf in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.
Induced emf `prop` Rate of change of magnetic flux
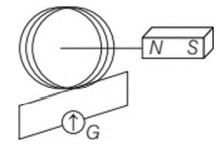
On the basis of Faraday’s law, current in the coil is larger
Options:
(a) when the magnet is pushed towards the coil faster
(b) when the magnet is pulled away the coil faster
(c) Both( a) and ( b)
(d) Neither ( a) nor ( b)