Induced Current
The steady current in the coil `C_2` as shown below produces a steady magnetic field. As coil `C_2` is moved towards the coil `C_1`, the galvanometer shows a deflection. This indicates that electric current is induced in coil `C_1`. When `C_2` is moved away, the galvanometer shows a deflection again, but this time in the opposite direction. This deflection is based upon the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
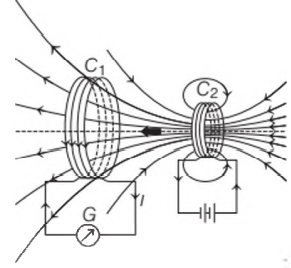
The change in magnetic flux
Options:
(a) decreases the radius of the coil `C_1` to half the initial radius
(b) induces emf in the coil `C_1`
(c) increases the radius of coil `C_1` to double the initial radius
(d) None of the above