Projectile motion is a form of motion in which an object or particle is thrown with some initial velocity near the earth’s surface and it moves along a curved path under the action of gravity alone. The path followed by a projectile is called its trajectory, which is shown below. When a projectile is projected obliquely, then its trajectory is as shown in the figure below
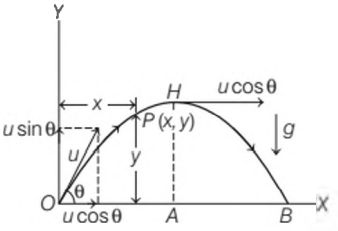
Here velocity `u` is resolved into two components, we get (a) `u cos theta` along `OX` and (b) `u sin theta` along `OY`.
In above case, the distance from the thrower to the point where the ball returns to the same level will be
Options:
(a) 39m
(b) 69m
(c) 68m
(d) 72m