Electric Dipole
An electric dipole is a pair of point charges with equal magnitude and opposite in sign separated by a very small distance. The mid-point of locations of `-q and q` is called the centre of the dipole.
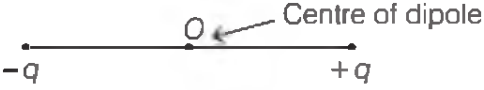
The strength of an electric dipole is measured by a vector quantity known as electric dipole moment `(p)` which is the product of the charge `(q)` and separation between the charges `(2l)`.
In most molecules, the centres of positive charges and of negative charges lie at the same place, hence their dipole moment is zero. `e.g. CO_2, CH_4`. However, they develop a dipole moment when an electric field is applied. But some molecules have permanent dipole moment, e.g. `H_2O` which are called polar molecules. If the centre of mass of positive charges coincides with the centre of mass of negative charges, the molecule behaves as a non polar molecule.
Dipoles in an electric field undergo
Options:
(a) magnetism
(b) electromagnetism
(c) magnetisation
(d) polarisation