Equipotential Surface
In physics, the region in space where every point in it is at the same potential, is called equipotential or isopotential. An equipotential region of a scalar potential in three-dimensional space is often an equipotential surface, but it can also be a three-dimensional region in space. The gradient of the scalar potential is everywhere perpendicular to the equipotential surface, and zero inside a three-dimensional equipotential region. In case of electrical conductors, if a and b are any two points within or at the surface of a given conductor, and given there is no flow of charge being exchanged between the two points, then the potential difference is zero between the two points. Thus, an equipotential would contain both points a and b as they have the same potential.
The figure given below shows various equipotential surfaces.
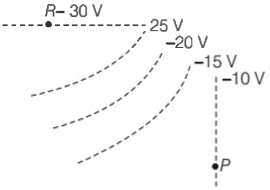
What is the direction of electric field E at P and R ?
Options:
(a) At P,E is to the left and at R,E is upward.
(b) At P,E is to the right and at R,Eis downward.
(c) At P,E is to downward and at R,E is to the left.
(d) At P,E is to upward and at R,E is to the right.